Subscribe to Vetline
Keep up to date with LIC's products and services.
And receive the quarterly Vetline newsletter.
To book an Animal Health test online, please click the link below:
Animal Health Booking Vet Form
Subscribe to Vetline
Subscribe to our quarterly Vetline newsletter to keep up to date with the latest news about LIC products and services.
BVD - Webinar
View the recording of the BVD - Vet webinar
Topics covered
- BVD Bulk tank milk result interpretation
- New BVD Status product
- Changing to Wet TSU's, what this means for vets
- Trial for BVD testing on Wet TSU's for calves under 35 days old
BVD testing for calves – Webinar
View the recording of the BVD testing for calves Webinar
Topics covered
- BVD PCR test using tissue samples
- Trial data for BVD Ag ELISA & PCR testing for calves
- Difference between wet & dry tissue sampling units(TSU’s)
- Q & A
Johne’s disease – Webinar
View the recording of the Johne’s disease webinar
Topics covered
- Johne’s disease timeline
- Johne’s diagnostics testing with LIC
- New data reporting for Johne’s disease
- Johne’s disease research at LIC
- Johne’s disease farmer success stories
MINDA Reproduction provides comprehensive information about a herd’s reproductive performance. By using MINDA Reproduction you are able to monitor the herd throughout their reproductive cycle from pre-mating through to mating and calving to identify any potential issues in a timely manner.
Download the guide to the Reproduction tile in MINDA for detailed explanations on the data available and some rules of thumb to help with your data analysis.
In August this year, we will be offering a new and improved test to help you better detect mastitis in your herd.
The Mastitis Multiplex PCR test provides more information and greater accuracy at a lower cost and will replace LIC’s existing Staph. aureus PCR test.
Click here to learn more.
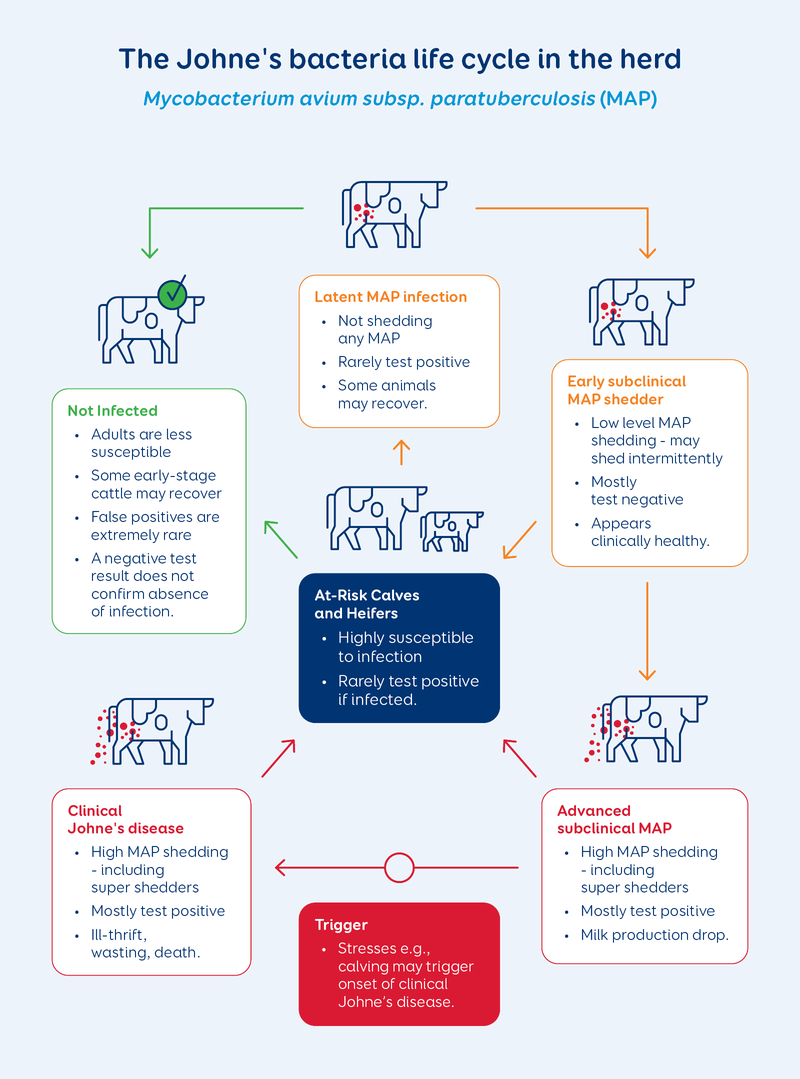
Johne’s disease is a chronic infection caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP). This bacterium infects the gut of cattle and other ruminant animals, causing the intestinal wall to gradually thicken and become inflamed. This results in leakage from the gut wall and prevents the animal from absorbing vital nutrients.
Johne’s disease is widespread amongst NZ dairy herds. Most infected herds harbour low levels of MAP bacterium with occasional clinical disease. In some herds Johne’s disease becomes problematic with annual losses of 1% and more in the milking herd.

What are the symptoms?
Johne’s disease may lead to:
- ill thrift
- lower milk production
- difficulty reproducing
- weight loss
- diarrhoea
- swelling under the jaw, also known as ‘bottle jaw’.
How is it spread?
Johne’s disease is primarily spread through faeces and ingested by animals through contaminated pasture, colostrum/milk, feed, and water.
Infected cows start shedding bacteria some time before clinical signs of disease appear. As the infection progresses, increasing amounts of bacteria are excreted in the faeces of heavy shedder cows. Calves may pick up the infection in the calving paddock and remain at risk if they are exposed to faeces or effluent from the adult herd. Cows with advanced infection (both clinical and subclinical) can also transmit the bacteria to the unborn calf in utero and via colostrum or milk.
How can Johne’s disease be managed / controlled?
During the early stages of Johne’s disease, infection diagnostic tests are unreliable, so controlling it can be a challenge. It is possible to minimise the impact of Johne’s disease by reducing the exposure of young stock to the disease. The severity of Johne’s disease in an individual (i.e., time until clinical signs develop and the amount of faecal shedding) depends on several factors including the age when infection occurred, the amount of bacteria ingested and the number of times the animal has been exposed to Johne’s disease bacteria. Therefore, any management measures that reduce exposure (e.g., avoiding effluent paddocks and paddocks grazed by the adult herd) will help limit disease spread.
Risks and control measures can vary from farm to farm. Keys to a successful risk management plan are:
- eliminating the source of bacteria by early removal of clinical Johne’s disease cows and other high-risk shedders
- removing susceptible calves and young stock from possible sources of infection as soon as practicable.
Convenient testing
LIC offer Johne’s testing for dairy cows on herd test milk samples to identify high-risk cows with advanced Johne’s disease. These cows shed high numbers of bacteria and are a major cause of the spread of the disease to other animals, especially young stock. This testing may detect “super–shedders” that are not showing signs of the disease at the time of testing, but are likely to develop clinical Johne’s disease in future.
Test limitations and timing
The Antibody ELISA test detects the immune response of the animal to MAP infection. While it generally does not identify cows during early stages of subclinical infection (i.e., low-risk non-shedders or intermittent/low shedding), the test performs very well in advanced stages of Johne’s disease.
The test will identify 8-9 out of 10 cows with clinical disease, or those that are excreting large amounts of bacteria (heavy and super shedders).
You can test at any time of the year, but we recommend focusing on the second or third herd test (November-March). Although you can test at the first or fourth herd test, please note false positives may occur if:
- cows have recently calved (within 7 days of herd test)
- SCC is >1 million
- low milk volumes - avoid testing too close to dry off or when part of the herd has dried off.
Risks
Testing for Bovine Tuberculosis (TB) before the herd test may increase the number of uninfected animals being given a suspect result in Johne’s disease ELISA testing. The risk for false positive or false high positive results may also be increased. TB tests can affect blood serum Johne’s disease ELISA, therefore any confirmation testing completed after the herd test may be impacted.
Our advice aligns with UK recommendations to leave the following gaps between your TB test date and JD ELISA test:
- 43 days before milk JD ELISA
- 71 days before blood JD ELISA.
Where possible, TB testing should be done after JD ELISA to avoid any possible issues.
For more information download the TB test interference with JD ELISA-Literature Review.
Blood testing for individual animals
We also offer a blood test to identify individual animals with Johne’s disease.
Blood samples are taken from animals showing symptoms of Johne's disease, or from a selection of animals to find out how widespread the problem is.
We need a 10ml blood sample from each animal being tested. We prefer purple top blood tubes but will accept red top tubes.
Send the blood samples to our laboratory, together with a completed Animal Health Sample Submission form
Tick Johne's disease ELISA to indicate the test you want.
Further information
For further information, please contact LIC's Animal Health Team on 0800 436 362 or email [email protected]

Take advantage of the growing international demand for A2 milk by using our A2 gene test to identify A2 cows. About 30% of New Zealand dairy cows produce A2 milk. It contains a protein called A2 β- casein. A1 milk contains A1 β- casein, or a mix of both A1 and A2 β- casein. Some consumers are willing to pay more for A2 milk because they believe it prevents the digestive problems they say they experience after drinking A1 milk. We do not endorse any of the claims made about A2 milk. If you want to set up an A2 herd, every animal in the herd must have the A2 gene. You must also breed with bulls that have the A2 gene.
Tests to obtain an A2/A2 result
Animals already G3 profiled can obtain a retrospective result - 5-7 working days
Combine the A2/A2 test with DNA parentage testing - 4-5 weeks
Combine the A2/A2 test with your regular herd test - 10 working days
Standalone A2/A2 test on a tissue sample - 3 weeks
For information about taking samples and submitting samples, view our A2/A2 test page.
Download a PDF about A2/A2 testing.
BVD Brochure-Learn how to protect your herd from BVD
Download the BVD Animal Health Brochure and learn how to protect your herd.

Test for BVD using milk samples
We offer three BVD testing options that use milk samples to monitor your herd’s BVD status and identify persistently infected (PI) animals for culling.
- BVD Status Pack - combines both products below for a superior BVD test at both a herd and individual animal level. Test three bulk milk (vat) samples throughout the season to monitor your herd’s BVD status as well as individually test all cows present at the herd test to obtain lifetime BVD status on MINDA.
- Bulk Milk BVD Monitoring Pack - test three bulk milk (vat) samples throughout the season to monitor your herd’s BVD status.
- BVD PI Hunt - test milk samples from a routine herd test to identify PI animals if you get a positive result from your first two Bulk Milk BVD Monitoring tests.
BVD Status pack to monitor your herds BVD Status and obtain lifetime BVD status of individual cows
How the test pack works
1st test - Bulk Milk (early season)
- Tests for BVD virus (PCR test) and antibody exposure levels (Antibody ELISA)
- Results emailed.
2nd test - Herd test milk samples (approx 2 weeks after 1st bulk milk)
- Each sample tested for BVD virus (PCR test)
- Results will be emailed and uploaded to MINDA - animals are permanently marked in MINDA as Not Persistently Infected (NPI) or Persistently Infected (PI). This is a lifetime status.
3rd test - Bulk Milk (4 weeks after herd test)
- Tests for BVD virus (PCR test) to check PI animals have been removed from the herd.
- Results emailed.
4th test - Bulk milk (late season)
- Test for antibody exposure levels (Antibody ELISA)
- Results emailed.
Results
- The turnaround time for results will be within 5 working days for the bulk tank milk samples and within 7 working days from when you receive the herd test lab strip result for the individual herd test results. Results will be emailed and uploaded to MINDA.
- The PCR test results (for bulk milk samples and individual herd test samples) will be either BVD positive or negative.
- The Antibody ELISA test for bulk milk samples gives you an indication of the herds’ immunity. There are 5 possible results: No exposure, low, medium, high or very high exposure.
- All individual BVD positive results are tested twice to confirm result.
Order a BVD Status Pack
You can order a BVD Status Pack by:
- calling 0800 436 362
- talking to your LIC rep
- completing a BVD Status pack order form- Farmer and emailing it to [email protected]
- asking your vet to complete a BVD Status Pack order form - Vet and email it to [email protected].
Once signed up this pack will rollover each year.
For more information, download the BVD status info sheet.
Bulk Milk BVD Monitoring Pack to monitor your herd’s BVD status
We test three bulk milk samples over a six-month period.
We get the bulk milk samples from your dairy company at the following times:
- September to October (before mating).
- A fortnight later to check whether the results have changed.
- Late February to early March to check for any changes in your herd’s BVD status after natural mating bulls have been with the herd.
We test the first two samples for:
- the BVD virus (PCR test)
- the antibodies animals produce in response to the virus (antibody ELISA test). The higher the antibody levels the more likely your herd is currently infected, or has been recently infected.
We test the third sample for BVD antibodies only.
If the BVD virus is detected in both the first and second tests we recommend a PI Hunt test to identify which animals are causing the problem. This allows you to cull PI animals before mating and reduce the risk of cows being exposed to the BVD virus during early pregnancy.
Invest in the pack annually for best results
Invest in a Bulk MiIk BVD Monitoring Pack every year to get a regular update on your herd’s BVD status — including its antibody levels. Low antibody levels indicate that your herd has a low natural immunity to BVD and may be vulnerable to infection. Talk to your vet about what you can do to protect your herd.
Results
We’ll email the results to you up to3-5 days after we receive the bulk milk samples. We can also send the results by post if you don’t have email.
One-off bulk milk sample tests
We also offer two types of one-off bulk milk sample tests to monitor BVD in your herd:
- A one-off bulk milk test uses a bulk milk sample ordered from your dairy company to check your herd’s BVD status.
- A custom sample milk test uses a sample of milk you collect yourself. It may include milk from a smaller number of animals to narrow down the source of infection. Call us on 0800 436 362 to find out how to collect the milk sample.
Use the tests to detect:
- the BVD virus (PCR test) or
- BVD antibodies (antibody ELISA test).
Order a Bulk Milk BVD Monitoring Pack
You can order a Bulk Milk BVD Monitoring Pack by:
- calling 0800 436362
- talking to your LIC rep
- completing a Bulk Milk BVD Monitoring Pack order form — Farmer and emailing it to [email protected]
- asking your vet to complete a Bulk Milk BVD Monitoring Pack order form — Vet and email it to [email protected].
Use these order forms to order a one-off bulk milk test or a custom sample milk test too.
Download a PDF copy of BVD Brochure - Learn how to protect your herd from BVD.
BVD PI Hunt — identify PI animals for culling
Test individual milk samples from a routine herd test to identify PI animals so you can cull them and protect your herd.
Book a BVD PI Hunt test if the BVD virus is detected in your first two Bulk Milk BVD Monitoring tests.
You can test for the BVD virus in every milk sample from the herd test, or you can test samples from selected cows, such as heifers. Talk to your vet or our Animal Health Advisors team about which cows you should test.
Results
We’ll email the results to you up to 5-7 days after we receive the milk samples. We can also send the results by post.
Book a BVD PI Hunt test
Call 0800 436362 to book a PI Hunt test.
Test for BVD using blood and tissue samples
We offer several tests that use blood and tissue samples to identify PI animals so you can cull them and protect your herd.
Use these tests to:
- identify PI animals in your milking herd
- screen new additions to your herd
- screen calves and yearlings
- screen natural mating bulls before introducing them to your herd.
BVD testing using tissue samples
Detect the BVD virus in individual animals by using our tissue test. If you're DNA parentage testing, you can also add BVD testing onto this.
What test you're getting and how old your animals are will determine what tissue sampling unit (TSU) you need to use - wet or dry.
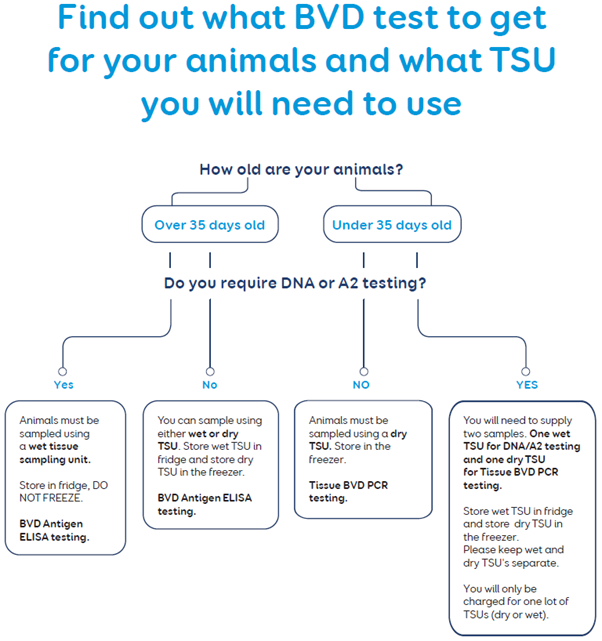
See Collecting tissue samples for A2 gene testing or BVD testing for information about how to collect and send tissue samples for standalone BVD testing, and how to combine the BVD test with DNA parentage testing.
Use the GeneMark Genomics Sample Submission form to test for the BVD virus in tissue samples collected for DNA parentage testing.
Use the Animal Health Sample Submission form to test for the BVD virus in tissue samples collected for standalone BVD testing. Tick BVD Antigen ELISA or Tissue BVD PCR on the form.
We’ll send you the results from BVD Ag ELISA testing in 3 working days and Tissue BVD PCR results in 6 working days.
More information about Wet TSU’s.
More information about BVD testing calves.
BVD testing using blood samples
Detect the BVD virus in calves before they are 35 days old with blood samples taken by your vet.
You can also use blood samples as an alternative to tissue samples to test for the BVD virus in individual animals, or to measure their exposure level or immunity status.
Your vet should collect a 10ml blood sample for each animal being tested. We prefer purple top blood tubes but will accept red top tubes.
Choose from three tests:
- BVD PCR — detect the virus in animals over 35 days old.
- Calf PCR — detect the virus in calves less than 35 days old.
- BVD antigen ELISA — detect the virus in animals over 35 days with a slightly faster turnaround time for results.
Send the blood samples, with a completed Animal Health Sample Submission Form, to:
LIC Diagnostics
140 Riverlea Road
Hillcrest
Hamilton 3216
Tick the box on the form to indicate which of the tests you want.
We’ll send you the results in 3 to 5 days, depending on which of the tests you choose.

Milk Pregnancy Testing (MPT) for dairy cows is a hassle-free option for non aged pregnancy diagnosis.
MPT utilises a Herd test milk sample to detect pregnancy associated glycoproteins produced by the placenta.
MPT has great benefits:
- Detects pregnancy from 28 days after mating
- Easy and Convenient
- Non invasive
- Pregnancy results uploaded to MINDA Live and reported via email.
- Test your whole herd or a select group of animals at the herd test(partial herd* - minimum 25 samples).
The Milk Pregnancy Test has been validated for herd test milk samples against veterinary pregnancy diagnosis.
Results
Turnaround time for results is approximately 5-7 working days (from when the herd test lab strip is released).
The results report will be directly emailed to the farmer.
The report will have 3 possible outcome categories:
- Pregnant
- Re-Check
- No Pregnancy Detected
Animals in the Re-check category should have Pregnancy diagnosis confirmed by other means.
Results will be uploaded to MINDA Live with the following categories:
- Pregnant MPT
- Re-Check
- Empty *
* If an animal has been tested within the 28 days of their last mating, an empty result may be given.
Test Limitations
- The Milk Pregnancy Test does not age pregnancy
- The Milk Pregnancy Test accurately detects pregnancy 28 days after mating
- All customers are subject to eligibility criteria and lab capacity
- On average, the percentage of animals falling into the Re-check category was 1.86% during trials – however, this can vary from 0% to 10% for individual herds
Risks
False positives may occur if an animal has recently aborted (it can take at least two weeks for pregnancy protein levels to drop following a slip). If the herd test date falls within this period this animal may still give a ‘Pregnant’ result.
Further Information
For further information, please contact the Animal Health Advisor’s team at LIC on 0800 436 362 or email [email protected]
Download a PDF about Milk Pregnancy testing.
Complete the Animal Health Sample Submission Form if you are sending blood or tissue samples to test for:
- Johne’s disease in individual animals
- BVD in individual animals.
- Enzootic Bovine Leukosis (EBL)-Please note samples will be pooled but resulted individually
Animal Health Sample Submission form
Johne’s disease blood test
Tick Johne’s disease ELISA on the Animal Health Sample submission form to test for Johne’s disease in blood samples from individual animals.
BVD blood tests
Choose from one of four BVD blood tests:
- BVD PCR — detect the virus in animals over 35 days old.
- Calf PCR — detect the virus in calves less than 35 days old.
- BVD antigen ELISA — detect the virus in animals over 35 days with a slightly faster turnaround time for results.
- BVD antibody ELISA — test whether an animal has been exposed to the BVD virus.
BVD tissue test
Tick BVD antigen ELISA on the submission form to test for the BVD virus in tissue samples from animals over 35 days old.
Tick Calf BVD PCR on the submission form to test for the BVD virus in tissue samples for animals under 35 days old.
Animal Health Sample Submission form
Courier your form
Courier the samples, with the completed forms, to:
LIC Diagnostics
140 Riverlea Road
Riverlea
Hamilton 3216
A2A2 Herd Testing Submission form
Animal Health Sample Submission form
Bulk Milk BVD Monitoring Pack order form — Farmer
Bulk Milk BVD Monitoring Pack order form — Vet
BVD Status Pack Submission Form - Farmer
BVD Status Pack Submission form - Vet
GeneMark Genomics - Account application form
Subscribe to Vetline
Keep up to date with LIC's products and services.
And receive the quarterly Vetline newsletter.